No hay productos en el carrito.
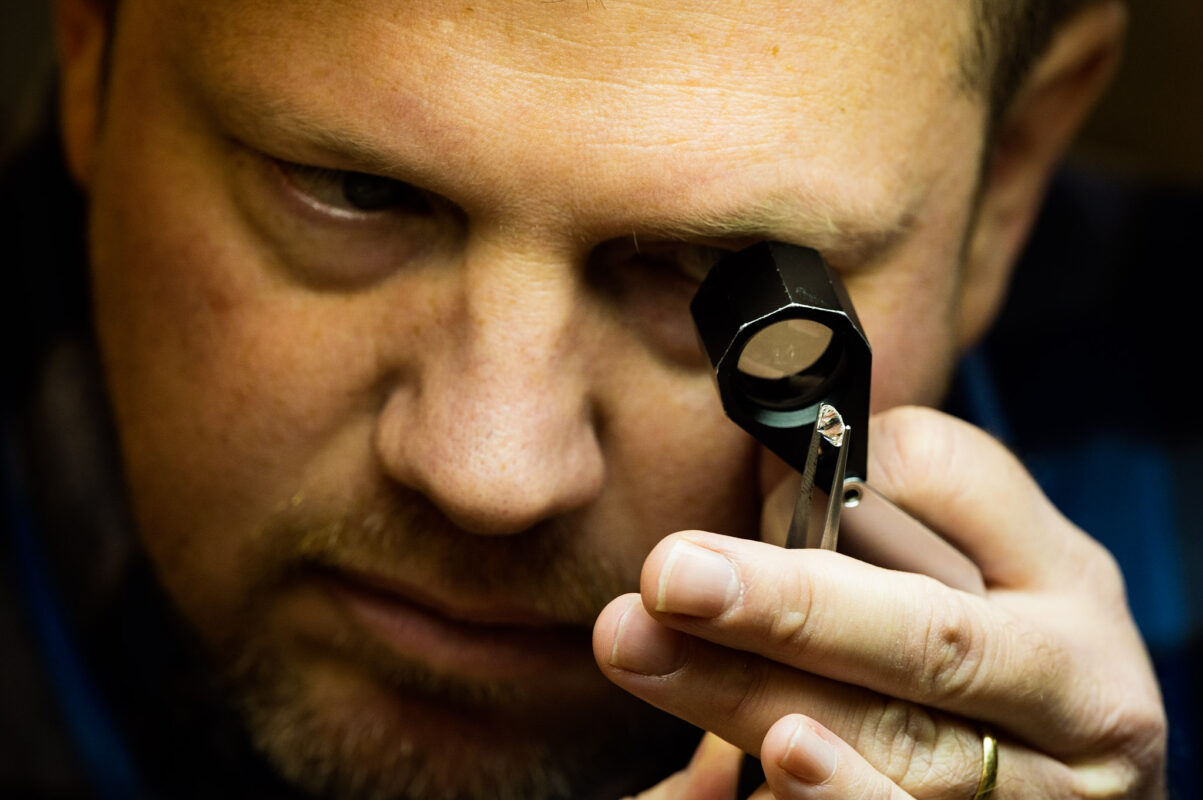
Humans have spent thousands of years entranced by gemstones and precious metals. In some ways, we’re like fish – we’re attracted to shiny things! That’s why jewelry and gemology are such fascinating subjects with rich histories. It’s also why it’s so difficult to tell the real deal from the imitation. While costume jewelry and diamond alternatives are beautiful accessories, they won’t get you the cash that a *real* piece of jewelry will. Here are our tips to distinguish the real jewelry from the fake… and how to know when to seek a professional’s opinion. Precious Metals While we see today’s Olympic champions bite their gold medals, we don’t suggest this course of action for actually testing whether or not your gold is real. The history of the “gold bite test” dates back to merchants who would trade gold coins for goods. If their bite left teeth marks, the coin was deemed a fake since forgers would alloy their gold coins with other metals, including lead. In fact, some Olympians have even chipped their tooth whilst chomping down on their hard-earned medals! So, please (please) don’t do this. There’s a much easier (and dentist-approved) way to test the validity of the precious metals in your jewelry: look for stamps. Jewelry will often have teeny-tiny marks stamped on them in order to indicate their metals and fineness. We suggest getting our your readers for this. Here are some popular marks and what they mean: Metal US Fineness Marks International Fineness Marks 9- or 10-karat gold 9K or 10K 375 (37.5% pure gold) or 417 (41.7% pure gold) 14-karat gold 14K 585 (58.5% pure gold) 18-karat gold 18K 750 (75.0% pure gold) 24-karat gold 24K 999 (99.9% pure gold) Platinum PT 950 Sterling Silver 925 or sterling 925 Some jewelry pieces are unmarked, or the mark might be damaged. In this case, you can always bring the piece into one of our locations for a free check – no appointment is needed. Diamonds vs. Diamond Alternatives While metals have markings that can help the average consumer distinguish the real from the imitation, diamonds are a little trickier. An untrained eye can typically spot a real diamond, however there are a few diamond simulants that can dupe jewelry enthusiasts: Cubic Zirconia (or CZ) If you’ve ever shopped for an engagement or wedding ring at a big box store, you might know that CZ is used to simulate a diamond to visualize what it would look like in a certain setting. There are a few key differences to distinguish CZ from a real diamond. First, the dispersion of a CZ is much higher than that of a diamond. This means that the CZ will break up the light into a larger spectrum of colors than a diamond will. Second, most CZs are completely colorless. This is rare in real diamonds – a colorless diamond falls into the D color category on the diamond color scale. Even really stunning diamonds will have a twinge of yellow, while you won’t typically see this in CZs. Synthetic Moissanite This is a relatively newer diamond alternative that has recently gained popularity. Similar to the CZ, it also has more dispersion than that of a natural diamond. Natural moissanite is so rare, that if you’re looking at moissanite in jewelry, odds are that it’s synthetic. According to Brilliant Earth, “The most effective way to tell moissanite apart from a diamond is to use a loupe to look through the top, or the crown, of the jewel at an angle. You will see two slightly blurred lines that indicates a double refraction, an inherent quality of moissanite.” White Sapphire or White Topaz Unlike the previous alternative, white sapphire and white topaz will have less dispersion than a natural diamond. Glass Glass is more transparent than diamond. Another easy way to tell the difference is to check for inclusions Most diamonds will have inclusions that can either be seen with the naked eye or with a jeweler’s loupe. Glass will not have any inclusions as it will be hand-cut to simulate a diamond. Lab-Grown Diamonds You might be asking, “what about lab-grown diamonds?” Well, lab-grown diamonds technically are diamonds. However, since they’re man-made and manufacturing is ever-growing, they don’t fetch the same prices as natural diamonds since they are easier to come by. In fact, it’s often speculated that the value of these man-made alternatives will go down rather than up like their natural counterparts. Lab-grown diamonds can fool cheap diamond testers, so if you’re wondering whether or not yours was grown in a lab we recommend bringing it in for a closer look. Emeralds, Sapphires, and Other Gemstones There aren’t really any great DIY tests for gemstones, so the simple answer to this is just to bring it in to one of our GIA Graduate Gemologists. They’ll easily be able to distinguish real gemstones from imitations. While we don’t typically purchase pearls, there is a DIY method to check if they’re real or not. While we don’t encourage using your teeth to test gold, it is okay to use your teeth to test pearls. Simply rub the pearl against your teeth! If it feels grainy, you’ve got a genuine pearl on your hands. If it feels smooth, odds are that it’s not real. Other Tips to Distinguish Real Jewelry From The Fake We always recommend bringing in an item for our experts to take a look at, especially if you wish to sell it. Whether you sell it to us or not is up to you – and we’ll look at it for free, so there’s nothing to lose. You can visit us at any of our DFW locations in Dallas, Euless, Frisco, Grand Prairie, Grapevine, and Lewisville – no appointment needed.